

Low pollution is a crucial advantage of combined cycle plants that burn natural gas. Hydroelectric plants are by their nature limited to operating at sites with sufficient water flow. In addition, such plants are often built near collieries to minimize the cost of transporting coal. įor example, coal power plants are built away from cities to prevent their heavy air pollution from affecting the populace. Efficiency gains no longer come from increasing generating capacity, but from smaller units located closer to sites of demand.
#DEMAND RESPONSE HOMER ENERGY DRIVER#
Thus, the grid had become the main driver of remote customers’ power costs and power quality problems, which became more acute as digital equipment required extremely reliable electricity. These economies of scale began to fail in the late 1960s and, by the start of the 21st century, Central Plants could arguably no longer deliver competitively cheap and reliable electricity to more remote customers through the grid, because the plants had come to cost less than the grid and had become so reliable that nearly all power failures originated in the grid. Central plants are usually designed to take advantage of available economies of scale in a site-specific manner, and are built as "one-off," custom projects. These were developed when the costs of transporting fuel and integrating generating technologies into populated areas far exceeded the cost of developing T&D facilities and tariffs.
These, in turn, supply the traditional transmission and distribution (T&D) grid that distributes bulk power to load centers and from there to consumers. Historically, central plants have been an integral part of the electric grid, in which large generating facilities are specifically located either close to resources or otherwise located far from populated load centers.

is the uncertain nature of such electricity resources. One of the major issues with the integration of the DER such as solar power, wind power, etc.

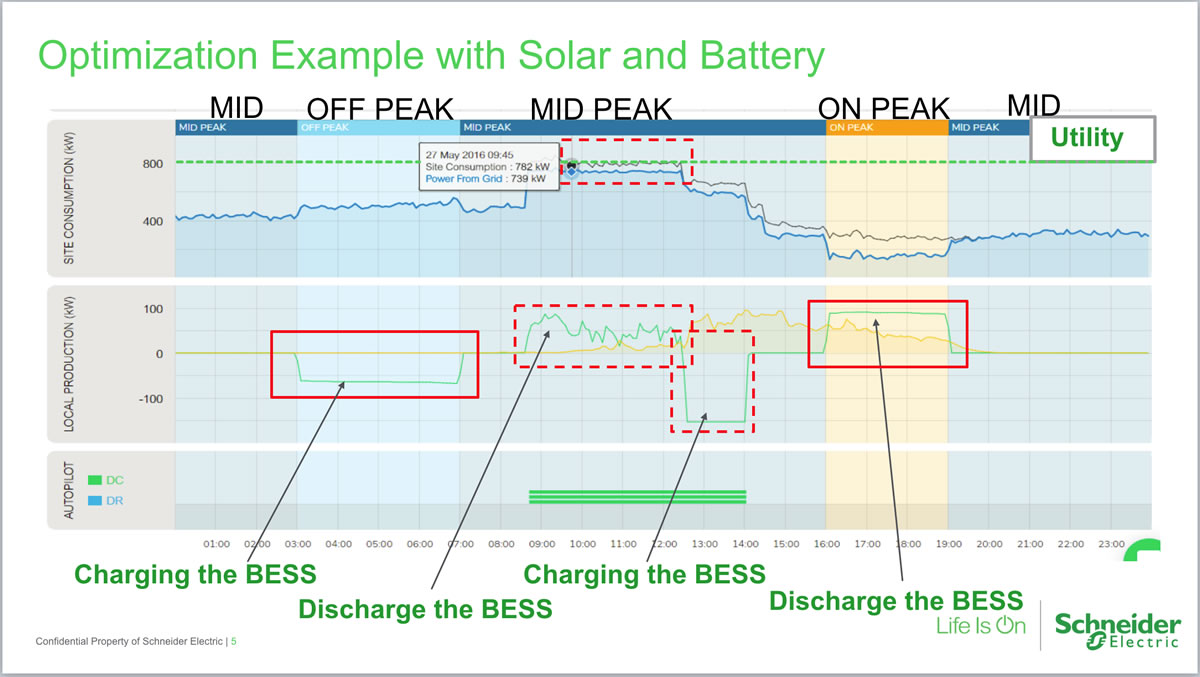
Distributed generation and storage enables the collection of energy from many sources and may lower environmental impacts and improve the security of supply. By means of an interface, DER systems can be managed and coordinated within a smart grid. A grid-connected device for electricity storage can also be classified as a DER system and is often called a distributed energy storage system ( DESS). These systems can comprise multiple generation and storage components in this instance, they are referred to as hybrid power systems.ĭER systems typically use renewable energy sources, including small hydro, biomass, biogas, solar power, wind power, and geothermal power, and increasingly play an important role for the electric power distribution system. By contrast, DER systems are decentralized, modular, and more flexible technologies that are located close to the load they serve, albeit having capacities of only 10 megawatts (MW) or less. Ĭonventional power stations, such as coal-fired, gas, and nuclear powered plants, as well as hydroelectric dams and large-scale solar power stations, are centralized and often require electric energy to be transmitted over long distances. Distributed generation, also distributed energy, on-site generation ( OSG), or district/decentralized energy, is electrical generation and storage performed by a variety of small, grid-connected or distribution system-connected devices referred to as distributed energy resources ( DER).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
